Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Calculation of the Covariance Matrix¶
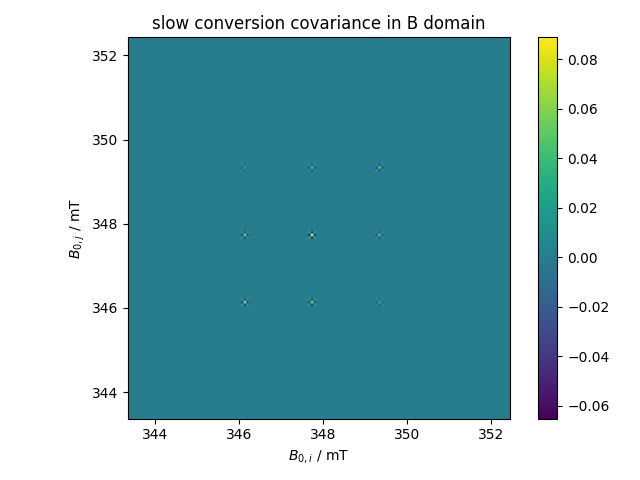
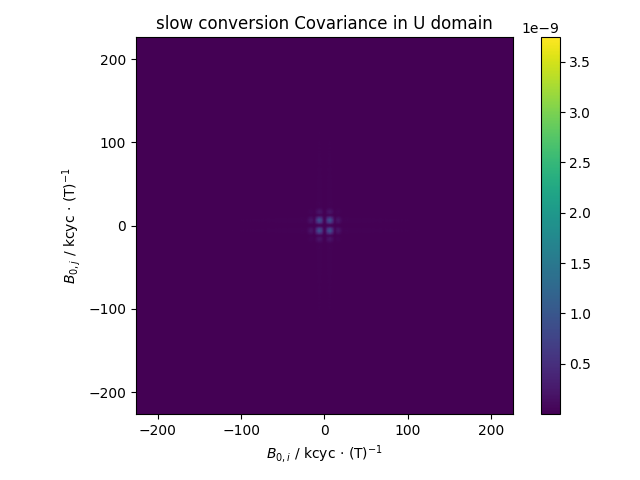
After rescaling plots, the covariance matrix is calculated and then plotted for a 2D Field experiment (spectra as a function of field with multiple collections or “Times”)
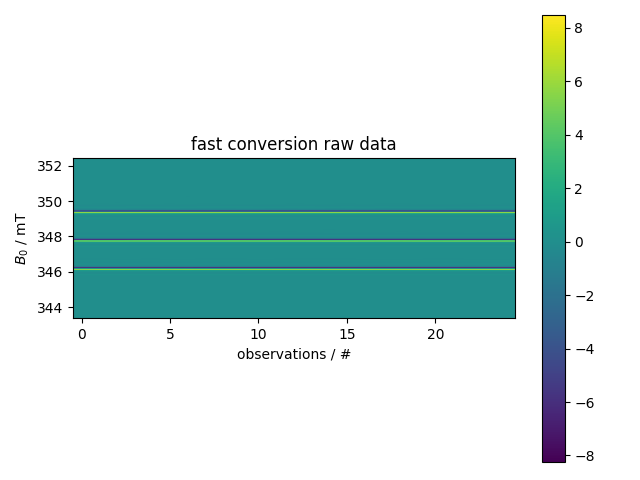
1: fast conversion raw data |||('s', 'mT')
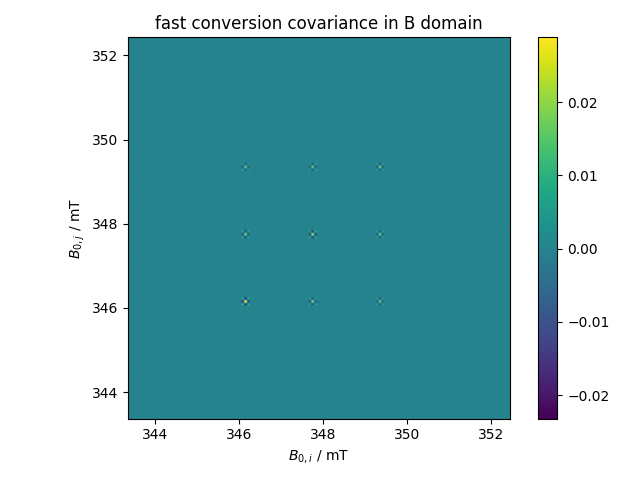
2: fast conversion covariance in B domain |||('mT', 'mT')
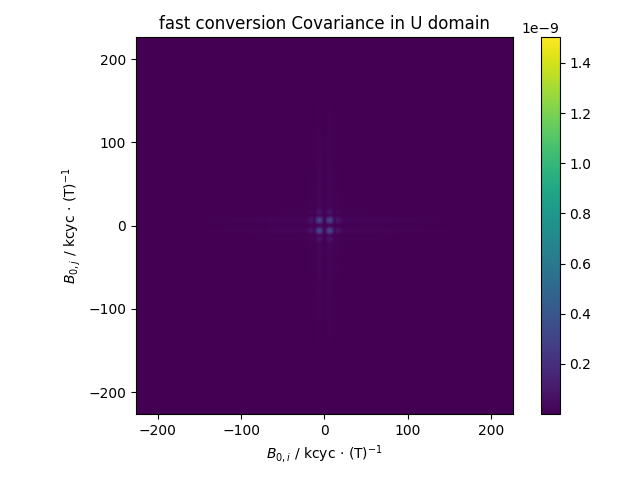
3: fast conversion Covariance in U domain |||('kcyc · (T)$^{-1}$', 'kcyc · (T)$^{-1}$')
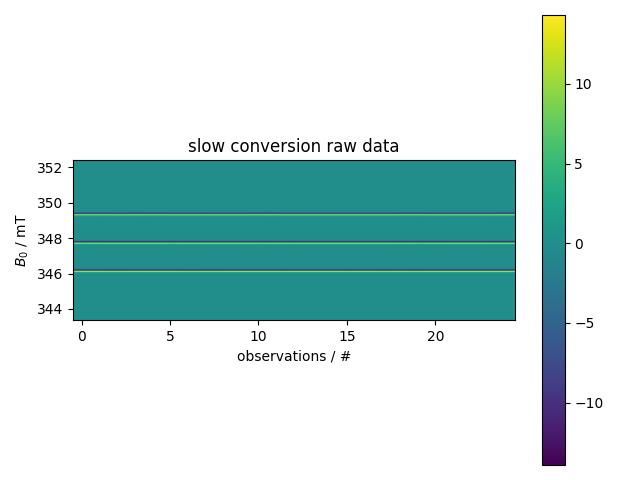
4: slow conversion raw data |||('s', 'mT')
5: slow conversion covariance in B domain |||('mT', 'mT')
6: slow conversion Covariance in U domain |||('kcyc · (T)$^{-1}$', 'kcyc · (T)$^{-1}$')
from pyspecdata import *
from pylab import *
fieldaxis = "$B_0$"
exp_type = "francklab_esr/romana"
with figlist_var() as fl:
for filenum, (thisfile, fl.basename) in enumerate([
(
re.escape("250123_TEMPOL_100uM_AG_Covariance_2D.DSC"),
"fast conversion",
),
(
re.escape("250123_TEMPOL_100uM_AG_Covariance_2D_cc12.DSC"),
"slow conversion",
),
]):
d = find_file(thisfile, exp_type=exp_type)["harmonic", 0]
d.set_units(fieldaxis, "T").setaxis(fieldaxis, lambda x: x * 1e-4)
d.rename("Time", "observations")
d.reorder([fieldaxis,"observations"])
fl.next("raw data")
fl.image(d)
fl.next("covariance in B domain")
# we do this first, because if we were to ift to go to u domain and
# then ft back, we would introduce a complex component to our data
fl.image(d.C.cov_mat("observations"))
d.ift(fieldaxis, shift=True)
fl.next("Covariance in U domain")
fl.image(
d.cov_mat("observations").run(abs)
) # this time, do not spin up an extra copy of the data
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 20.872 seconds)